Carcinoma cervix
Carcinoma cervix
- 1,25,000 new patients in India every year
- Incidence varies from 15 – 48 / 100,000 women
- Carcinoma cervix is preventable
- Health education
- Screening programmes
- Risk factors for Carcinoma cervix
- Early age at intercourse
- Repeated / Frequent births
- Multiple sexual partners
- HPV infections (Type 16 & 18 highly oncogenic)
- Low socio-economic status
- Smoking
- Site
- Ectocervix 80%
- Endocervix 20%
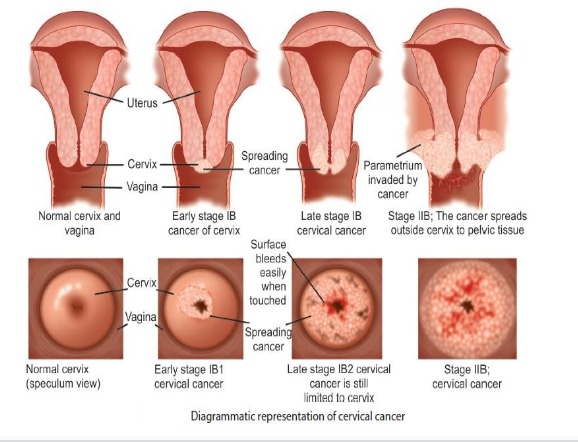
- Gross lesion
- Occult
- Proliferative : Friable growth
- Ulcerative : Erodes the cervix to form an irregular crater
- Infiltrative : Expands the cervix
- Histopathology
- Squamous cell carcinoma (80-90%)
- Large cell keratinizing
- Large cell non-keratinizing
- Small cell
- Adenocarcinoma (10-20%)
- Endocervical
- Clear cell
- Adeno-squamous
- Adeno-acanthoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma (80-90%)
Diagnosis of carcinoma cervix
- Clinical (Stage Ib1 onwards)
- Early symptoms
- Abnormal bleeding
- Post coital
- Inter-menstrual
- Post-menopausal
- Abnormal discharge
- Blood stained
- Dirty
- Foul smelling
- Abnormal bleeding
- Late symptoms
- Pelvic pain
- Urinary symptoms
- Rectal symptoms
- Early symptoms
- Signs
- Abnormal area / growth on cervix
- Induration
- Friability
- Bleeding on touch
- Fixity
- Confirmation of diagnosis
- Diagnosis is confirmed by Histopathological examination of the biopsy sample
Prevention of Carcinoma cervix
- Health education
- Avoid early marriage
- Avoid early intercourse
- Avoid promiscuity
- Proper hygiene
- Use of barrier contraception
- Screening programs
- Screening for pre-malignant lesions
- Screening for early diagnosis
Investigations
- For confirmation of diagnosis
- Biopsy
- From obvious growth or abnormal area
- Directed biopsy in very early lesions
- Cone biopsy
- Biopsy
- For staging of disease
- Intravenous Urography
- Abdominal Ultrasonography
- Cystoscopy
- Proctosigmoidoscopy
- Examination under anaesthesia (EUA)
- CT / MRI
- Base line investigations of general condition